Psoriatic Arthritis
Introduction
Psoriasis is primarily a skin disease. There is increased turnover of skin. Sites most commonly affected are knees, elbows, umbilicus or navel etc. Nail changes are also frequent. It is a disease of the immune system of human body. The immune system is deranged and fails to identify the body’s own cells and mounts an attack on them leading to inflammatory changes in the skin and other organs. It can affect other organ systems also. Most commonly it affects joints. Condition is called psoriatic arthritis. It is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects connective tissues like ligaments and muscle tendons and joints. It affects both men and women aged between 30 and 50 years. Presenting features involve progressive joint pain, crippling, scaly red patches etc. It is a debilitating condition. Treatment most commonly is symptomatic and supportive. Drugs most commonly used are pain killers and steroids that suppress the overactive immune system.
Iranian scientists have moved to the forefront in embryonic stem cell research, according to a recent joint study by Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
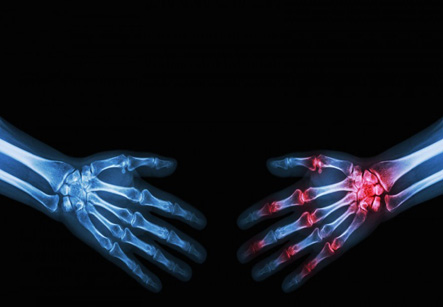
Treatment
Recently several data are available regarding application of stem cell therapy in various immunological diseases. Limited studies have proved that stem cell therapy is effective in psoriatic arthritis. This approach is kept reserved for non-responders. Patients, who have failed to respond adequately to surgeries, long term use of expensive medicines, long term use of steroids or pain killers etc. are suitable for this option. Stem cell therapy in psoriatic arthritis is still in its infancy. However initial results are encouraging.
However there have been very few attempts at stem cell therapy in psoriasis and long term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in this area remain to be seen.
Adult stem cells from bone marrow are collected and harvested. Embryonic stem cells may be gathered from umbilical cord blood right after the birth of the baby. These cells have the capacity to differentiate and grow into cells of bones and cartilages like osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Once they are extracted they are cultured in the laboratory and made to grow into these cells. After these cells are reintroduced into the body there is formation of new bones and cartilages. As a result there is improvement of signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. There is remission of pain and swelling, improves mobility of joint and gradual improvement of the disease condition.
Successful stem cell therapy can have various advantages. There will be decreased use of supportive medicine like pain killers etc. that have a higher incidence of side effects. Cause of the disease can be eradicated with stem cell therapy. However there have been very few attempts at stem cell therapy in psoriasis and long term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy in this area remain to be seen.