Neurological Disease
Introduction
Many common incurable neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, are caused by a loss of neurons and glial cells. In recent years, the stem cells are used successfully to regenerate the neurons and glia in culture. This has led to advances in stem-cell-based transplantation therapies for human patients. More recently, efforts have been taken for stimulating the formation and preventing the death of neurons and glial cells produced by endogenous stem cells (the stem cells present within the adult central nervous system). The researchers are trying to translate these exciting advances from the cultures in laboratory into clinically useful therapies for patients suffering from severe neurological disorders. These therapies may prove essential in medicine, as most of these neurological diseases do not have cure and cause significant debility in patients.
There are many different types of stem cells. Some of these stem cells are very useful within stem cell treatment, whereas others are less useful or potentially harmful.
Iranian scientists have moved to the forefront in embryonic stem cell research, according to a recent joint study by Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
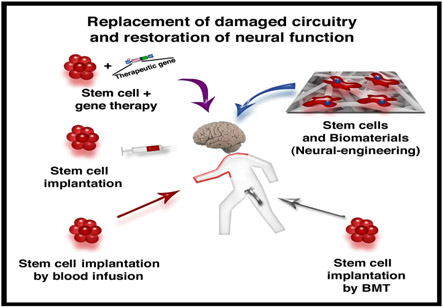
Neurological diseases involve a vast number of disorders affecting the brain, the spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. These diseases have some common features such as neurological dysfunction, slow and progressive deterioration, and extensive loss neurons). However, these diseases are different in terms of their pathogenetic mechanisms and complexity. Therefore, for any stem cell therapy to be effective in treatment of neurological diseases, such therapy needs to be carefully tailored to the specific dysfunctions involved.
Procedure:
Stem cells are emerging as one of the most exciting new areas of neuroscience. These cells help in revealing many secrets about normal development, but also as therapeutic agents for a range of neurological diseases. Stem cells may have critical influence in neurological practice in future as they can provide insights into mechanisms of disease as well as curative strategies. However, the development of such therapies will require patience and any translation of the laboratory efforts to actual patients should be undertaken very slowly and based on sound experimental data. A failure in doing so will not only discourage the researchers involved in this type of therapy, but also will reduce the hopes of many patients and their neurologists.
The Central Nervous System is an immunologically privileged organ where there are various natural barriers to the development immune responses. Therefore, the grafted cells are postulated to be able to survive in the CNS for a long period of time. The transplanted immature (stem) cells also proliferate and elaborate cell growth factors in the brain lesions.
The adult bone marrow- derived cells can be used to treat neurological disorders. However, before being transplanted, the cells are tested for viruses to be safe. The cells can be grafted into the subarachnoidal cavity of a patient via a lumbar puncture. The neurological benefits from the stem cell- based therapy tend to develop over a long period of time.
Results:
The results point out a high efficiency of applying the stem cell-based treatment in SCI patients. The majority of such patients noticeably improved the quality of their life Noteworthy is that the appreciable benefits from the stem cell-based treatment were noted not only in the patients with recent traumas, but also in whom with time periods after SCI of 1.5 years and longer, and who, in terms of conventional medicine, are considered as incurable.
The stem cell-based therapy may be effectively applied during immediate period after severe brain injure when the patient is unconscious. Such therapy can improve the level of consciousness, reduces risk of a lethal outcome, and promotes the neurological rehabilitation following the treatment. There are significant benefits from this treatment regarding the long-term consequences of hemorrhagic or ischemic cerebral strokes and quality of life of the patient.
The stem cell-based therapy may be effectively applied during immediate period after severe brain injure when the patient is unconscious.
Very impressive results were obtained in children with cerebral palsy. The stem cell-based therapy has helped the majority of CP patients to reduce their neurological defects and to reduce their dependence upon overall assistance markedly. There are also positive results obtained in case of treatment for congenital diseases such as spinal amyotrophy and Down’s syndrome, which are incurable diseases yet.
However, the stem cell-based treatment is met with limited success in the cases of degenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease as there are chronic pathological processes underlying these diseases.