Intradiscal Electrothermal Therapy IDET
Introduction
Intradiscal electrothermic therapy (IDET) is a relatively new, minimally invasive approach for spinal disc-related chronic low back pain. This type of persistent disc pain is usually caused by nerve fibers that have grown away from their normal location into the outer layers of the disc. It can also occur due to degeneration of the tough outer layer (called as annulus) of the disc. Injury to the disc can cause the material in the center of the disc (called as nucleus) to rupture or herniate into the outer layers of the disc. This material from the nucleus can irritating the outer layers containing nerves and causes pain. Before IDET, an investigation called as discography is generally done to identify the possible disc problem. After discography, it can be decided by the doctor whether the specific disc problem can be treated by IDET.
Indications:
IDET is used to treat selected patients of chronic disc-related low back pain in whom symptoms are not relieved even after 3 to 6 months of conservative treatment.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide spinal surgery in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
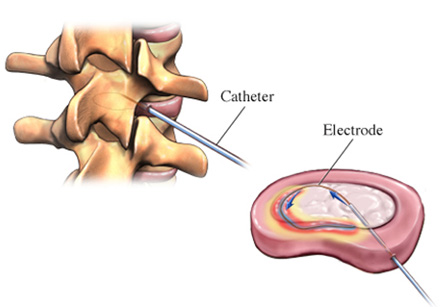
Procedure:
1. Before an IDET procedure, the patient is given local anesthesia and a sedative medication.
2. Under the guidance of “live” X-ray imaging (fluoroscopy), the surgeon inserts a hollow needle containing a flexible tube (called as catheter) and heating element into the spinal disc.
3. Then, the catheter is positioned in a circular fashion in the outer layer (annulus) of the disc. The catheter is slowly heated to about 194 degree F (or 90degree C). The heat destroys the nerve fibers and toughens the disc tissue. Any small tears present may also be sealed by heat.
4. Antibiotics are given either intravenously or directly injected into the disc to prevent a disc infection.
After Surgery:
Pain relief after IDET is not immediate. Instead, pain may increase during the first couple of days. Physical therapy is needed during recovery. During the first month after IDET, walking and easy stretches are usually advised. During the first 2 to 3 months, exercises schedule should be followed as directed, and lifting, bending, and long periods of sitting is avoided.
Strenuous sports such as skiing, running, tennis should be avoided for at least 5 to 6 months after IDET.
Risks
Complications of IDET are possible, but uncommon. Some complications are:
1. Nerve damage.
2. Disc injury
3. Disc infection
Discography may also increase the risk of disc problems in the future. If the doctor recommends a discography, experts recommend getting a second opinion before the test.
Results:
Long-term efficacy of the procedure has not been studied as most people do not meet the requirements for this procedure. Some research has suggested that IDET is a safe and effective treatment for people who fit the criteria for the procedure. However, more research on IDET will show the effectiveness of this procedure more clearly.
Criteria for IDET:
Before considering IDET, it should be made sure that you are a good candidate for the procedure as well as the doctor doing the procedure is well trained and experienced in this field. In case of any doubts related to suitability of the procedure, getting a second opinion is a prudent choice.
Criteria for deciding who might be a good candidate for IDET are discussed below.
1. The patient is considered as a candidate for IDET if:
2. The age is at least 18 years.
3. There is persistent disc-related pain for several months. Some studies suggest pain to be present for at least 3 months, but many suggest 6 months.
4. The symptoms have not improved with at least 6 weeks of conservative treatment, including pain relievers, physical therapy or a home exercise program for low back pain.
5. Pain involves mostly in the low back, not the leg.
6. Pain is worst while sitting.
7. The damage is at the back of the outer layer (annulus) of the degenerated disc.
The patient is probably not a candidate for IDET if:
1. The patient does not meet all the criteria to be eligible for IDET
2. There is severe disc degeneration or there is not enough space to insert the needle for the IDET procedure (as found on discography).
3. There is spinal stenosis.
4. There is associated spondylolisthesis.
5. The patient has another medical condition that can increase the risk of surgery or may make the follow-up care difficult.