Discectomy
Introduction
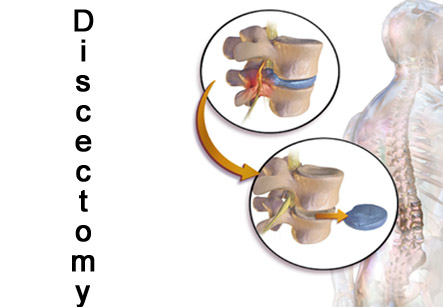
Discectomy is a surgical procedure to remove herniated disc material which is pressing on a nerve root or the spinal cord.
Before removal of the disc material, a small piece of bone called as the lamina, is also removed from the affected vertebra. This is called a laminotomy or laminectomy. It allows better visualization of the herniated disc.
Microdiscectomy is a procedure which uses a special microscope to view the disc and nerves. This larger view can allow the use of a smaller incision.
During discectomy, the surgeon removes the part of the disc that is herniated and is pushing into the spinal canal. Any loose fragments of disc are also removed.
This surgery is done under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. Overnight stay is usually required after the surgery.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide spinal surgery in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
After the surgery:
After surgery, the patient is encouraged to get out of bed and walk as soon as the effect of anesthesia wears off. Prescription medicines may be advised to control pain during post-operative period.
Recovery:
Sitting may not be comfortable at first. Most people avoid having to sit for longer than 15 or 20 minutes. This improves over time.
Walking is advised as often as possible for the first several weeks. This reduces the risk of forming too much of scar tissue.
Sedentary office work can be resumed in 2 to 4 weeks. If the job requires physical labor (such as lifting or operating machinery that vibrates), you can be able to go back to work 4 to 8 weeks after surgery.
Many people are able to resume work and daily activities soon after surgery. In some cases, the doctor may suggest a rehabilitation program. This may include physical therapy and home exercises.
Indications:
1. Surgery is usually performed to decrease pain and also to regain normal movement and function.
2. Pain in the leg, numbness, or weakness which can make the patient unable to perform the daily activities.
3. The leg symptoms which do not get better after at least 4 weeks of conservative treatment.
4. Weakness of legs or loss of motion found on physical examination which is likely to get better after surgery.
5. Surgery is considered as an emergency option in case of caudaequina syndrome. Signs of this syndrome include:
• Recent loss of bowel or bladder control.
• Recent onset of weakness in the legs (usually both legs).
• New numbness or tingling in the buttocks, genital area, or legs.
Results:
Although surgery does not benefit every patient, it works well for many people. Discectomy may provide faster pain relief than nonsurgical treatment. When conventional open discectomy is compared with microdiscectomy, people have reported being equally satisfied with both the techniques.
Risks:
As with any surgery, there are some risks. These include:
1. Failure of the purpose of surgery or no more benefit than other type of treatments.
2. Slight risk of damaging the spine or nerves.
3. Infection
4. Risks of anesthesia.
Variations or methods of discectomy:
Discectomy may be performed alone or along with spinal fusion. Spinal fusion is a procedure that joins the vertebral bones together in the back. It is sometimes effective for neck disk problems. A cervical or neck discectomy is usually combined with a fusion. However, for involvement of the low back (lumbar spine), the procedure is controversial and complex and is not commonly performed with a discectomy.
Many people are able to resume work and daily activities soon after surgery.
Percutaneous discectomy is a procedure using a special tool through a small incision in the back to remove or cut out the herniated disc. Percutaneous discectomy is considered less effective than open discectomy. All percutaneous methods rely on the posterolateral approach to the disc under local anesthetic supplemented with light sedation to avoid inadvertent root injury.
A newer form of discectomy using laser beams (laser discectomy) is still in the research stage. This procedure is performed by inserting a 18 gauze 7 inch long needle in the nucleus of the disc and applying Nd:YAG or KTP laser through the disc. The needle is placed under careful radiological guidance and all equipments for an open surgery are kept ready.