Arthritis of the Spine
Introduction
Arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder which can affect any joint in the body, including the joints in the spine or vertebral column. Spinal arthritis usually occurs in the facet joints (also called as inter-vertebral joints). These joints connect adjacent vertebrae together and are located in the posterior portion of the spine. Facet joints are important to facilitate movements in the spine such as bending, twisting, and stretching. However, these joints can thicken and harden with age, which can lead to arthritis. In arthritis of spine, the facet joint becomes inflamed and there is breakdown of cartilage in these joints. This can cause slight to severe pain, which can sometimes radiate to other areas of the body such as the buttocks or upper thighs. Progressive joint degeneration can create even more frictional pain. The resulting back pain can decrease range of back motion and flexibility while standing, sitting, and even walking.
Arthritis of the spine is a very painful and debilitating condition that often affects individuals above 40 years of age. If left untreated, this can lead to physiological problems such as muscle breakdown or weakness. Additional psychological problems such as anxiety and depression can also arise. Sometimes, a person with arthritis of the spine can suddenly develop excruciating pain which can make the patient bedridden and unable to perform normal daily activities.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide spinal surgery in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
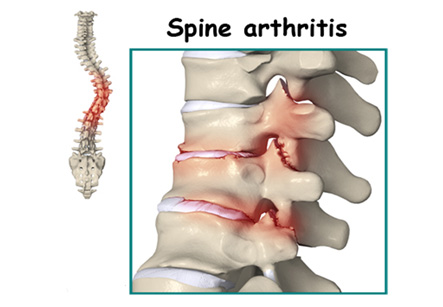
Causative and associated factors:
Increasing levels of stress, imbalances in hormone level, and nutritional levels are considered as associated conditions with spine arthritis. The causes may vary from person to person, but usually degeneration in the bones is an important factor. Sometimes past injuries or surgeries are blamed for spine arthritis. Compression of nerves due to herniated disks and bone spurs is also considered as an associated factor.
Symptoms:
Arthritis of the spine is a very painful and debilitating condition that often affects individuals above 40 years of age.
Classic symptoms of spine arthritis include pain and numbness in the back, neck, head, and shoulders. Type of symptoms may be different for different people, and their frequency and intensity can also vary. Bending and other everyday movements may also cause pain. Numbness is the neck area is very common. Other areas of body including the arms and legs may also experience numbness. In some cases, increased frequency of urination or the urgent need to urinate may occur.
Treatment
Conservative treatment:
Losing weight is considered as beneficial for treatment of spinal arthritis.
Exercises are an important way to battle arthritis. Exercise may be broken down into the following categories:
Strengthening exercises. These exercises can make the muscles supporting the joints stronger.
Aerobic exercises. These are exercises to make the heart and circulatory system stronger.
Range-of-motion exercises can increase the body’s flexibility.
Other non-drug treatments available for osteoarthritis include:
1. Massage
2. Acupuncture
3. Heat or cold compresses, which refers to placing ice or hot compresses onto the affected joint
4. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) using a small device which emits electrical pulses onto the affected joint.
5. Nutritional supplements
6. Pain medications may also be used to treat arthritis. Over-the-counter products include acetaminophen.
7. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are also available over-the-counter. These include aspirin, naproxen sodium, and ibuprofen. Uncommon side effects of NSAIDs include stomach irritation and bleeding, and less frequently, kidney damage.
8. Topical ointments and creams are also available to treat pain which can be applied to the skin in the area that hurts.
9. Prescription medications such as painkillers, mild narcotics, or oral steroids can be helpful. Injections of corticosteroids into the joint or into the space surrounding the spinal cord are being used for treatment. These treatments often do not correct the underlying problem and also do not have clear indications of long-term benefit.
Surgery:
Most cases of spinal arthritis can be treated without surgery, but surgery is sometimes performed. Spinal arthritis is one of the causes of spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal. Indications for surgery include impaired bladder and bowel function, damage to the nervous system, or severe difficulty in walking and moving around.