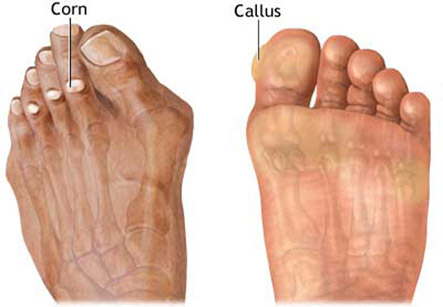
Corns
Introduction
Corns are areas of thickening of skin on the feet which can cause local pain in the feet. The predisposing factor for corns is excessive pressure or friction on the skin which is common in feet. Poorly fitting shoes is very important reason. A podiatrist can pare or remove the corns and can advise about the footwear, shoe insoles and foot padding for their prevention.
Types
In corns, the thickening of skin can press on the deeper layers of skin and can be painful. They are usually round in shape. There are two types of corns:
1. Hard corns- They are found on the smaller toes or on the outer side of the little toe. Poorly fitted shoes tend to rub in these areas the most.
2. Soft corns- They form in between the toes. Most common location is between the fourth and fifth toes. These are softer because of the sweat between the toes maintains moisture. Soft corns can become infected.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide Podiatry-Chiropody treatments in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
Causes of corns
The small bones of the toes and feet tend to stick out near a small joint or at a broad end. This causes extra rubbing and pressure on the skin over them. The constant rubbing on the skin causes it to thicken. This may lead to formation of corns.
The common causes of rubbing are
1. Tight or poor fitting shoes
2. Excessive walking or running
3. Deformities of bones of the feet.
Symptoms of a corn
1. Hard growth on the skin of toes
2. Pain on pressure
3. Swelling and redness around the lesion
4. Discomfort while wearing tight shoes
Treatment for corns
Expert advice from a podiatrist is required for treatment of corns. Patients should not cut or pick the corns by themselves, especially if having diabetes or in old age. Advice and treatments usually include the following:
1. Paring and trimming
• The podiatrist or doctor can pair down the thickened skin of a corn using a scalpel or blade. Pain reduces after the pairing as the pressure on the underlying tissues decreases.
• Sometimes repeated trimming sessions are needed.
• Recurrence can be prevented by rubbing the thickened skin with a pumice stone or emery paper once a week. It can be done by the patient at home.
• Foot can be soaked in warm water for 20 minutes to soften the thick skin before using a pumice stone or emery paper.
• A moisturizing cream should be used regularly on a paired corn to keep the skin softened to prevent recurrence.
2. Footwear
• Poor fitting shoe is the most common cause of corns. A rough corner in the shoe can cause excessive pressure on sides of toes or feet.
• Soft heels, plenty of room for the toes and extra cushion can be useful for prevention of corns.
• Extra adjustments are needed in patients with abnormal deformities of toes such as hammer toe or claw toes. Special shoes can be advised by the doctor in such cases which are available at various centers.
• Cushioning pad or insole of the shoe can also provide benefit to the affected toe. For soft corns between the toes, a special sleeve is available which fits around the toe and reduces pressure as well as sweating in that area.
• Special toe splint can be useful to keep distance between two toes and allowing the corn to heal.
• Improved footwear can itself reduce the pressure on the toes and thus cure the corn. This can also prevent recurrence.
• Such basic adjustments can help to treat the corns easily.
Surgery
In case a bony foot deformity is causing recurrent corns, operation may be required. The surgeon may correct a deformed toe, or cut out excessive part of a bone that is sticking out from a toe. The surgeon decides about which procedure is required for a particular patient.
Complications
Complications can occur due to inadequate or improper treatment. Some of complications are:
1. Infection
2. Development of an ulcer
3. Abscess or cyst formation