Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Introduction
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to open up the air cells in the sinuses and their ostia (openings) with an instrument called as endoscope.
It is a very common and efficient surgical procedure. It is also called as functional endoscopic surgery to distinguish it from other conventional sinus surgical procedures.
Purpose:
The purpose of this surgery is to FESS is to reestablish the normal drainage of the paranasal sinuses. Normal function of the sinuses is maintained by its ventilation through the ostia or mouth-like openings and is helped by mechanism of muco-ciliary transport to maintain the constant flow of mucus out of the sinuses into nasal cavity. To prevent stasis of secretions leading to infection and inflammation, this ventilation is very necessary. The infection due to lack of ventilation is called as sinusitis. The sinus ventilation occurs through the ostia which open into the nose. The sinuses open into the middle meatuses or curved passages in each nasal cavity. These meatuses are covered by small bony processes of the ethmoid bone projecting in each nasal cavity and this is together are known as the osteomeatal complex. The hair-like cilia in the sinuses help in directing the flow of mucus toward the ostia.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide ENT surgeries in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
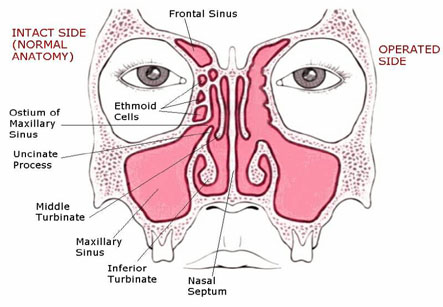
When sinusitis occurs may be from a throat or by dental infection, the cilia work less efficiently, causing stasis of secretions. The mucous membranes of the sinuses become inflamed and swollen leading to closure of ostia. This leads to bacterial infection.
During endoscopic sinus surgery, the surgeon uses an endoscope or small tube like instrument having a camera to view the inner cavities of the nose. Using special instruments, the sinuses are opened and problems inside are dealt with.
Advantages of endoscopic sinus surgery are:
1. It is minimally invasive surgery.
2. No incision is required.
3. Healthy tissues are not handled.
4. Less time is required than conventional surgery.
5. Recovery is faster.
6. Bleeding and scarring is minimized.
Diagnosis/Preparation:
1. Medical history is important part of the preoperative evaluation.
2. The ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist examines the sinuses by diagnostic procedures and imaging studies.
3. The fiber optic endoscope is used to examine the nose and all its sinuses thoroughly. The middle turbinate, middle meatus, any bony obstruction as well as presence of polyps.
4. CT scanning can be used to identify the diseased areas, to determine the extent and possible cause of the disease as well as for planning of surgery.
Description:
1. This surgery is done under general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation. The patient can usually go home on the same day after surgery.
2. Medications like epinephrine are applied topically during surgery to produce vasoconstriction.
3. Then, the surgeon locates the middle turbinate which is the most important landmark for endoscopic sinus surgery. The projecting bone on the side of the nose known as the uncinate process is removed.
4. The surgeon opens the ethmoid air cells in the ethmoid bone to facilitate the ventilation, but does not remove the mucosa over the bone.
5. After this the maxillary sinus is located and its ostium is checked for obstruction. This can be opened by a procedure known as middle meatalantrostomy if required.
6. Thus, this procedure improves the function of the sinuses by restoring the ventilation.
Aftercare:
1. The sinus pain after FESS is not severe. It can be relieved by simple pain killers.
2. The surgeon performs a cleaning procedure two to three times a week to prevent formation of crust in the nasal cavity. This can also be done at home by performing a simple nasal douching at least four times a day.
3. Normal function of sinuses reappears after one or two months.
4. In patients with severe sinusitis or polyps, a course of systemic steroids combined with antibiotics can hasten the recovery.
Risks:
1. The most serious risk associated with endoscopic sinus surgery is blindness resulting from damage to the optic nerve which is uncommon.
2. Cerebrospinal fluid leak is the most common major complication of FESS. The leak is can easily be repaired at the time of surgery.
3. Other rare complications are orbital hematoma and nasolacrimal duct stenosis.
4. Bleeding is a common risk for any surgery.
5. Anesthesia related risks like breathing problems and allergy to medications.
Results:
Resolution of sinusitis is considered as success of the FESS procedure. There is relief of nasal obstruction and facial pain. Both Caldwell-Luc operation and FESS both are equally efficacious but the patients prefer endoscopic surgery. The result of the surgery depends on the extent and severity of the disease. Therefore, the best results are obtained in patients with limited nasal sinusitis.