Direct Laryngoscopy
Introduction
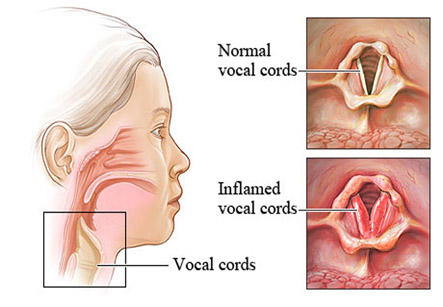
Laryngoscopy is an examination done by doctor of the back of the throat, larynx or voice box, and vocal cords with an instrument called as laryngoscope. Direct laryngoscopy is a method for seeing deep inside the throat with the help of flexible or rigid laryngoscope. The flexible scopes help to show the throat better and are more comfortable for the patients. Rigid scopes are mainly used in surgery.
Indications of direct laryngoscopy:
It is done for one of the following purposes:
Diagnostic:
1. To find the cause of voice problems like breathy voice, hoarse voice, weak voice, or no voice.
2. For diagnosis of cause of throat and ear pain.
3. To examine injuries of throat
4. To find the cause of difficulty in swallowing or a feeling of a lump in the throat.
5. To examine strictures in throat as well as blockage in the airway.
6. To diagnose the cancer of voice box.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide ENT surgeries in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible prices
Therapeutic:
1. As an aid in surgical procedure to remove foreign objects in the throat
2. To perform biopsy in the throat or laryngeal mass.
3. To remove polyps of the vocal cords
4. To perform laser treatment of lesions of larynx.
5. As an aid in therapy of laryngeal cancers.
Preparation for direct laryngoscopy
Before a rigid laryngoscopy, the following should be informed to the doctor:
1. Allergy to any medications
2. Having other diseases like heart disease, diabetes or high blood pressure.
3. Any medications being taken
4. Any blood clotting problems or if blood-thinning agents are being taken like warfarin
5. Smoking and alcoholism
6. The patient is or may be pregnant.
7. History of any surgery or radiation treatments to the mouth or throat.
Patient should not eat or drink anything for at least 8 hours before the procedure. A consent form is signed by the patient regarding the procedure and risks involved.
Procedure:
Direct flexible laryngoscopy
Patient should not eat or drink anything for at least 8 hours before the procedure.
A topical anesthetic medication is sprayedon the throat to numb it. A medication can be given to dry up the secretions in the nose and throat. Then, the surgeon puts a thin, flexible scope having a camera in the nose and then gently maneuvered in the throat. Then, the doctor examines properly the throat, voice box and surrounding structures.
Direct rigid laryngoscopy
1. All the jewelry, any dentures or removable braces should be removed before the rigid laryngoscopy.
2. It is done in a operation room under general anesthesia and medications to abolish laryngeal reflexes are given.
3. The rigid laryngoscope is then put in mouth and down the throat. The doctor then carefully examines the voice box (larynx) and vocal cords.
4. Foreign objects in throat or larynx can be removed, biopsies can be taken, and polyp removal as well as laser treatment can be done.
After the procedure:
1. The examination takes about 15 to 30 minutes. After the procedure, monitoring of the patient is done in the recovery room until the patient is fully awake and able to swallow.
2. Eating or drinking anything should be avoided for at least 2 hours after a laryngoscopy otherwise choking may occur. Sips of water should be taken initially followed by normal diet.
3. Some soreness can be common in throat after the procedure. Throat should not be cleared and coughing needs to be avoided for several hours.
4. Speak in normal tone of voice and for short time. Whispering or shouting can strain the vocal cords.
5. Sound may be hoarse for about 3 weeks after the laryngoscopy if tissues are removed.
6. If nodules or other lesions were removed from the vocal cords, total voice rest for up to 2 weeks is advised.
7. In case if a biopsy is taken, it is normal to spit up a small amount of blood after the laryngoscopy. Any difficulty breathing or excessive bleeding should be immediately informed to the doctor.
Risks
1. Swelling and blocking of the airway.
2. Spasm of laryngeal muscles.
3. If the patient already has partially blocked airway because of tumors, polyps, or severe inflammation of the tissues, there are higher chance of problems.
4. Complete blockage of the airway which is rare. In this case, the doctor may need to put a tube in the throat to help in breathing. Or, very rarely, a cut (incision) in your neck (a tracheotomy) is needed.
5. In case of biopsy, there is a possibility of bleeding, infection, or a tear in the airway.