Repair Femoral Neck
Introduction
Hip fractures in the elderly are most often caused by a fall, usually a seemingly insignificant fall. In younger patients with stronger bones, the common cause of a broken hip is usually high-energy injuries such as car accidents. Hip fractures can also be caused by bone weakened from tumor or infection, and this type of fracture is called as pathologic fracture.
A broken hip in the elderly can be explained primarily by weakened bones and osteoporosis. Other risk factors associated with hip fracture are female sex, Caucasian race; aesthetic built, and limited physical activity.
Femoral neck fracture occurs when the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint is broken from the femur. Treatment of a femoral neck fracture depends on the age of the patient and the amount of displacement of the fracture.
The important issue to be considered with femoral neck fractures is the disturbance of the blood supply to the fractured portion of bone due to injury. If the blood flow is diminished, these fractures are at high risk of not healing, especially in cases of badly displaced fracture. Due to this problem of blood supply, many cases of femoral neck fractures are treated by a partial hip replacement.
Iran ranks among the top 10 countries in orthopedics and Iranian surgeons perform high quality orthopedic surgeries at highly affordable prices
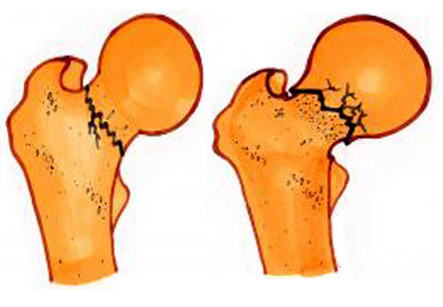
Treatment of a femoral neck fracture:
Treatment of a femoral neck fracture depends on several factors. The most important criteria to consider are the amount of displacement of the fracture and age of the patient.
The goals of treatment in patients with femoral neck fractures are to promote healing, to prevent complications, and to return function. This is completed with either surgical or nonsurgical management. Several factors must be considered before a treatment plan is recommended.
Physical therapy:
A physical therapist may be useful for reinforcing the physician’s instructions for rest and helping the patient to allow healing. In case of simple fractures, the mobility can be maintained by exercising the remaining extremities and performing non–weight-bearing strengthening activities that do not strain the affected hip joint. The physical therapist can evaluate the patient for any gait or anatomic abnormalities that may have led to the development of the fracture. Some patients may need orthotics to prevent excessive pronation, which causes increased stress on the femoral neck. The physical therapist focuses on patient education throughout the rehabilitation process, whether surgical or nonsurgical treatment is advised.
Surgical treatment:
In younger patients, who are under 60 to 65 years in this case, every effort is made to avoid a partial hip replacement. Hip replacements can work very well for less active patients, but they tend to wear out in younger and more active patients.
For most femoral neck fractures the treatment will be one of the following:
1. Hip Pinning
A hip pinning is a procedure which involves placing several screws across the fractured bone. It is generally only done in patients with a well-aligned and minimally displaced femoral neck fracture. Hip pinning may be attempted in young patients even if the bones are not properly aligned.
Femoral neck fracture occurs when the ball of the ball-and-socket hip joint is broken from the femur.
This procedure is performed usually under general or spinal anesthesia. A small incision is made on the outside of the thigh. Several screws are passed across the fracture for stabilizing the broken bones under fluoroscopic guidance.
Patients can generally place as much weight on the hip as is tolerated, but this can vary in some cases. The surgeon should be consulted before initiating any therapy or exercise. The primary concern with femoral neck fractures is the damaged blood supply to the bone which can lead to non-healing or bone death of the femoral head. In these cases, patients may require a hip replacement surgery in near future.
Hip Hemiarthroplasty
In this procedure, the ball of the ball-and-socket joint is removed and a metal prosthesis is implanted into the joint. Hip hemiarthroplasty is preferred in patients with displaced fractures as there is a risk of non-healing with trying to repair these fractures.
A hip hemiarthroplasty is performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. The surgeon makes an incision over the outside of the hip. The fractured femoral head is removed, and replaced with a metal implant. In a normal hip replacement surgery, the socket of the pelvis is also replaced. This is usually done only in patients of neck femur fracture with pre-existing arthritis of the hip. The prosthetic stem can be cemented into the bone in patients with osteoporotic bone, or press-fit in patients with better bone quality.
Rehabilitation
This is initiated almost immediately and patients can usually walk with their full weight on the implant. Patients usually feel much better after the surgery, and walking can be resumed quite quickly.