Hip Resurfacing
Introduction
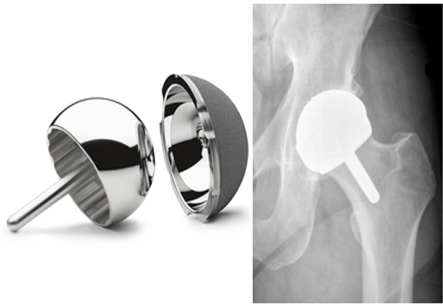
Hip resurfacing is a bone conserving procedure for hip replacement. In standard hip replacement, the surgeon replaces the acetabulum and also places the prosthesis in the femur. Hip resurfacing replaces the acetabulum in the same way but resurfaces the femoral head. Resurfacing means very little part of the femur is removed and replaced with the metal prosthesis.
This method does not violate the femoral canal.
This is indicated for young patients less than 55 years of age having osteoarthritis for maintaining an active lifestyle. It is a more conservative and less traumatic alternative to Total Hip Replacement.
Indications:
1. Arthritis in young age is the most important indication for the procedure. The joint surfaces become bare and rub on each other causing inflammation and pain.
2. Bone disorders of children like Perthe’s disease, dislocated hip, slipped epiphysis.
3. Abnormal growth of the hip like shallow socket causing arthritis
Iran ranks among the top 10 countries in orthopedics and Iranian surgeons perform high quality orthopedic surgeries at highly affordable prices
4. Trauma to hip
5. Infection
6. Avascular necrosis of the hip joint
7. Connective tissue disorders
8. Morbid obesity causing premature arthritis
Advantages:
1. This method does not violate the femoral canal. A total hip replacement can be done at a later date as the anatomy is preserved.
2. Less bone damage
3. Fewer complications
4. Faster recovery
5. Less hospital stay
Advantages over traditional THR:
Hip resurfacing is better than THR because of following points:
1. Preferred for younger patients
2. No femoral canal violation
3. Metal on metal articulation
4. More longer lasting
5. Less risk of dislocation
6. Minimal or no leg length discrepancy
7. Less risk of osteolysis
8. No thigh pain
9. Less restriction of activity
10. Revision is not usually required.
Before the surgery:
1. A proper history, examination and few lab tests and scans are done to determine the general health.
2. Patient should stop anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin at least a week before surgery.
3. Medications being taken for other conditions like diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure should be continued with advice from the treating doctor.
4. History of smoking or alcohol drinking should be told to the surgeon. Smoking should be stopped if possible as it interferes with the wound healing.
5. Recent history of cough, cold, fever, viral infections, or other illnesses should be informed to the surgeon.
Surgical Procedure:
1. An incision is taken over the hip to expose the hip joint.
2. The acetabulum is prepared for replacement using a special instrument called a reamer.
3. The acetabular prosthesis made of metal, plastic or ceramic is then inserted into the socket thus reamed.
4. Then, reaming of the thigh bone or femur is done using special reamers which take little bone.
5. The femoral prosthesis is inserted in the prepared femoral head.
6. The exposed hip is now reduced and then the muscles are closed in layers.
7. Incision is then closed with sutures and dressing is given to cover the wound. Small tubes are placed to drain any blood or fluids oozing out of the wound.
Post-Operative care:
1. Patient is shifted to recovery room and monitoring of vitals is done for at least half an hour.
2. Post-operative X-rays of the hip are taken.
3. On the following day, the drains are removed and patient can sit in bed.
4. Pain killers and antibiotics are given for a few days.
5. Post-operative physiotherapy is given to patient for early mobilization.
6. Patient is discharged after about 3 to 7 days depending on the patient condition.
7. Patient should start walking with the help of crutches by at least two weeks following the surgery and with a walking stick till 6 weeks.
Post-Op Precautions:
1. Patient should avoid the combined movement of bending the hip and turning the foot inward. It can cause dislocation.
2. Avoid sitting cross legged.
3. Low chairs and squatting positions should be avoided.
4. Elevated toilet sits should be used.
5. Shower should be taken after the wound healing.
6. If redness or swelling occurs in the wound or if there is fever, medical help should be called for.