Hip Replacement
Introduction
The hip joint is essentially a ball and socket joint with the upper end of the thigh bone or femur forming the ball and the acetabulum of the hip bone forming the socket. This joint bears most of the bodyweight and the joint surfaces are cushioned with cartilages for easy movement. Arthritis, injuries and severe damage to the hip joint can lead to the need for a Total Hip Replacement (THR). In this operation the surgeon replaces the ball and the socket with metallic replacements and the cartilage with artificial joint material. Before going in for a THR the surgeon will need to X ray of the joint to confirm that the pain is not due to any other pathology for example compressed nerves.
Surgery Procedure
Intravenous fluids and antibiotics will be given before surgery. A catheter will be placed in the bladder to drain the urine. Usually THR is done under general anesthesia where patient is unconscious and the muscles are relaxed to facilitate surgical intervention. The operation can also be performed under spinal or epidural anesthesia where the anesthetic medicine is injected into a space between the vertebrae in order to numb the legs during the operation without making one lose consciousness.
Iran ranks among the top 10 countries in orthopedics and Iranian surgeons perform high quality orthopedic surgeries at highly affordable prices
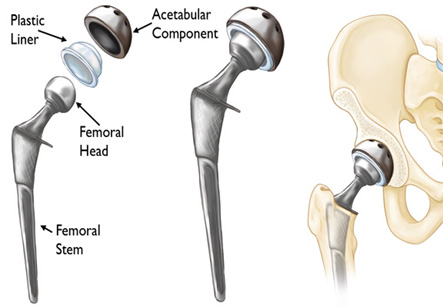
During the hip replacement operation an incision will be made on the affected hip joint and the affected portions of the hip bone and the femur will be sawed off. The new prosthetic parts will be attached to the bone with the use of bone cement. Once both the ball and the socket are in placed the damage cartilage is also replaced between the prosthetics. A test motion is usually done to check the proper placement of the prosthetics. A drain may be put to drain off the excess fluids from the operative site. The muscles and skin are then sutured back using sutures or staples. Patient may need a blood transfusion at this stage if they have lost a lot of blood during the operation.
Recuperation and post operative complications
After the surgery the patient will be transferred to the bed with a splint to hold the joint in place. They will have to stay in bed with a wedge shaped cushion to keep the hip joint in alignment. Fluids, analgesics and antibiotics may be given intravenously for a day or two before they can start on a normal diet and take the medications orally. Early physiotherapy ensures early mobility and rapid recovery. Within a day or two they will be encouraged to walk with the help of crutches, walker or a cane. Patient may be released from the hospital in a few days to a week.
Like any major surgery THR is also associated with the risk of pain, infection and bleeding. Nerves may also be compressed or damaged during the operation leading to pain in the post operative period.
The new hip is artificial and the muscles surrounding it are weaker than before the operation and so the hip may be easily dislocated.
The thigh bone or the hip may be fractured during or after the operation. This may be caused by other debilitating conditions of the bones like osteoporosis that renders bones brittle. THR raises the risk of the developing blood clots that can move up to the lungs or block the blood flow to the heart. This condition known as pulmonary embolism can be life threatening. Patient may be given medications to prevent these blood clots. Rapid mobilization can also protects from these blood clots and other complications like nerve compressions etc. The new hip is artificial and the muscles surrounding it are weaker than before the operation and so the hip may be easily dislocated. Patient is advised to avoid sitting too low, squatting or crossing the legs after the operation to prevent dislocation.
The benefits offered by the hip replacement operation are remarkable in terms of reduction of pain and thus improvement of sleep, improvement of range of motion, physical capabilities and quality of life.
THR has multiple surgical and non-surgical alternatives. Patient can go in for anti-inflammatory and pain reliving medication and regular physiotherapy to relive the pain and improve range of motion of the affected hip. Sometimes cortisone injections may also be given directly into the joint to relieve the pain and stiffness of the joint. Other surgical processes like hip resurfacing may also be tried. Here the implant is smaller and less of the bone is removed.