Bioprosthesis
Introduction
Knock knees and bow legs not only constitute a cosmetic problem – the misalignment of the axis can also result in knee problems.
Knock-knee is a state where the legs are bowed inwards in the standing position. It is also known as genu valgum. The bowing usually occurs at or around the knee, so that on standing with the knees together, the feet are far apart.
Bowleg is a state where the legs are bowed outwards in the standing position. It is also known as genu varum. The bowing usually occurs at or around the knee, so that on standing with the feet together, the knees are far apart.
The bioprosthesis is a successful procedure used for solving the problem of knock knees and bow legs. Correction of the leg axis is not a complicated procedure and treatment is similar to that used to mend broken bones. Even stressful sports can be resumed without problems after a rest period.
Iran ranks among the top 10 countries in orthopedics and Iranian surgeons perform high quality orthopedic surgeries at highly affordable prices
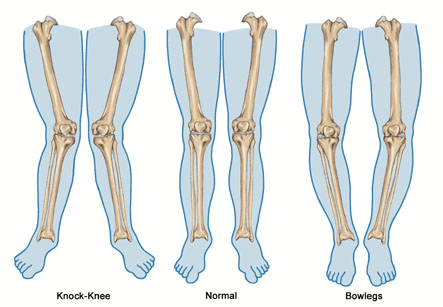
Causes of bowleg and knock-knee
Infants start out with bowlegs because of their folded position in the uterus. The infant’s bowlegs begin to straighten once the child starts to walk (at about 12 to 18 months). By age 3, the child becomes knock-kneed. When the child stands, the knees touch but the ankles are apart. By puberty, the legs straighten out and most children can stand with the knees and ankles touching (without forcing the position).
Knock knees can also develop as a result of a medical problem or disease, such as:
1. Blount’s disease (a condition of severe bowleg): Occurs usually in black children that is progressive, and may require surgery.
2. Post-trauma: where injury to the knee causes damage to the growth plate (also called the epiphyseal plate) and abnormal growth around the knee.
3. Growth disturbance or epiphyseal dysplasia, which may be a part of a generalized bone growth disturbance.
4. Rickets. Lack of vitamin D intake or inability to metabolize Vitamin D due to kidney disease can cause growth disturbance of the bones in the body, including the knee.
5. Injury of the shinbone (only one leg will be knock-kneed)
6. Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
7. Overweight or obesity
8. Rickets (a disease caused by a lack of vitamin D)
Knock Knees and Bow Legs (axial misalignment) cause problems with the knee
Both of these conditions lead to premature deterioration of the cartilage and the meniscus (the cushioning cartilage) in the knee joint. This, in turn, can develop into arthritis. Generally, only one leg is affected, and the uneven distribution of body weight further irritates the bad knee.
Indications for bioprosthesis
1. If the bowleg or knock-knee appears outside the age range (bowleg beyond age 3 and knock-knee beyond age 7)
2. If it is unilateral
3. If the inter-condylar or inter-malleolar distance is more than 2 inches or is rapidly progressing, i.e., more than ½ inches within six months
4. Associated symptoms like pain or limp
5. Signs of Blount’s disease, rickets or other disease syndromes
Treatment
1. In some cases, it is sufficient to treat only the cartilage deterioration through:
2. Abrasion- This stimulates the blood supply and thus the growth of new cartilage
3. The removal of stray bodies- This causes irritation, e.g. fragments of cartilage
• However, if this is insufficient, straightening of the leg may also be required. In this case, corrections must be made to the bone shape of either the upper (for knock knees) or lower (for bow legs) leg bone. This is done via a procedure similar to an artificial breakage whereby the shape is then corrected with plates and screws. The recovery procedure is also similar to that of a badly broken leg.
• Corrections to the bone shape of either the upper (for knock knees) or lower (for bow legs) leg bone.
Period of rest/ disability
The bioprosthesis is a successful procedure used for solving the problem of knock knees and bow legs.
Patients need to stay in the hospital for about a week post-procedure. They are also guided to build up the amount of weight they can put on their legs gradually. Patients normally require 6 to 12 weeks to be able to put their full weight on their legs. Physiotherapy is recommended during this period. Some patients may be advised to use crutches for safety while returning home from the hospital. Patients are requested to wait before they resume strenuous hind limb activities like- sports until the cartilage and bones heal sufficiently. This time frame may vary from patient to patient.
Advantages of bioprosthesis
1. Uncomplicated
2. stressful sports after a recovery period possible
3. brief recovery times