Anterior Cruciate Ligament
Introduction
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is usually the most commonly injured ligament of the knee. The most common cause of injury to this ligament is adventure sports and athletic activities. Nowadays, sports have become an increasingly important part of day-to-day life. Therefore, the number of ACL injuries has steadily increased.
After an ACL injury, the symptoms are swelling of the knee, feeling of unstable knee and pain during knee motion as well as while bearing weight. A cracking sound may be heard by many patients in their knee when an ACL injury occurs.
Depending on the severity of the ACL injury, treatment can include surgery to replace the torn ligament followed by rehabilitation exercises to regain the strength and stability. In case of the favourite sport is pivoting or jumping, a proper training program can help to reduce the chances of an ACL injury.
The torn ligament causes instability which leads to a feeling of insecurity and giving way of the knee.
Iran ranks among the top 10 countries in orthopedics and Iranian surgeons perform high quality orthopedic surgeries at highly affordable prices
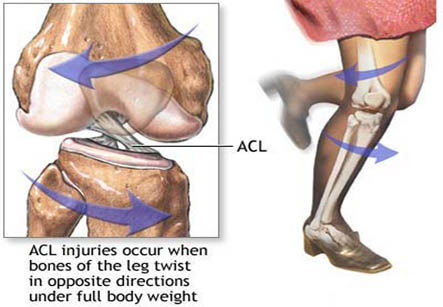
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue which connect the ends of two bones together. The ACL is located in the centre of the knee joint. It runs from the backside of the femur (thigh bone) to connect to the front of the tibia or shinbone.
The ACL runs through a special notch in the femur called as the intercondylar notch. It also attaches to a special area of the tibia called the tibial spine.
The ACL controls and limits the forward movement of the under the femur. If the tibia moves too far, the ACL tends to rupture. The ACL is also the first ligament that becomes tight when the knee becomes straight. ACL can tear if the knee is forced past this point, or hyperextended.
Other parts of the knee may be injured when the knee is twisted violently, as during a clipping injury in football. A tear of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) on the inside edge of the knee is also common. The lateral meniscus, which is the U-shaped cushion between the outer half of the tibia and femur bones can also be torn during sports injury.
Symptoms
The symptoms following a tear of the ACL can vary. Usually, there is swelling in the knee joint within a short time following the injury. This happens due to bleeding into the joint from torn blood vessels in the damaged ligament. The torn ligament causes instability which leads to a feeling of insecurity and giving way of the knee. This occurs especially when the patient is trying to change direction on the knee. The knee may feel like slipping backwards.
The pain and swelling from the initial injury usually subsides after two to four weeks, but the knee may still feel unstable. The main treatment is required for the symptom of instability and the inability to trust the knee for support. In modern orthopedics, the surgeons have realized that long-term instability of this joint leads to early arthritis of the knee.
Objectives of treatment for an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury are to:
• To restore normal or almost normal stability of the knee joint.
• Restore the previous level of function the patient was having before the knee injury.
• Limit loss of range of motion in the knee.
• Prevent further injury or more damage to other knee structures.
• Reduction of pain and swelling.
• Prevention of future osteoarthritis
Rehabilitation therapy is needed, whether or not the patient has surgery on the knee. Therapy can include:
• The use of temporary crutches or possibly, a knee brace
• Range-of-motion exercises to regain the full knee motion
• Muscle-strengthening and stability exercises
Surgical treatment
• Surgical reconstruction. A torn ACL can’t be successfully sutured back together. Therefore, the ligament is replaced with a piece of tendon from another part of the leg. This surgery is performed by an arthroscope through small incisions around the knee joint. A camera is used to guide the placement of the ACL graft.
• Arthrocentesis. An ACL injury causes bleeding inside the knee. This can lead to significant swelling. Arthrocentesis is done to reduce this swelling by a needle inserted into the knee joint to aspirate the excess fluid in the synovial cavity.