Brain Aneurysm
Introduction
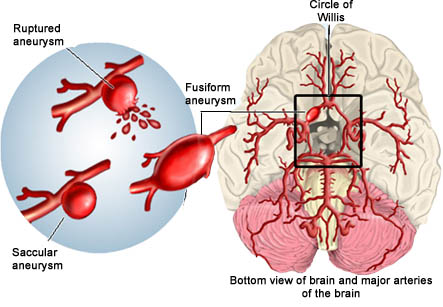
A brain aneurysm or cerebral aneurysm is a bulging or balloon like weak area in the wall of an artery that supplies blood to the brain. In most cases there are no symptoms and it is undetected until the brain aneurysm ruptures, releasing blood into the skull and causing a stroke. After rupture there is a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Depending on the severity of the hemorrhage, brain damage or death may result. The most common location for brain aneurysms is in the network of blood vessels at the base of the brain called the circle of Willis.
Causes of brain aneurysm
Aneurysms may develop in certain people due to genetic tendencies. In some people atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries due to high blood cholesterol or aging may lead to aneurysms. Women, high blood pressure, people of African descent, smokers etc. are at a higher risk of getting brain aneurysms.
Iran has made significant progress in neurosurgery and The world renowned Iranian scientist in neurological surgery Professor Majid Samii has garnered the 2014 Golden Neuron Award. We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide Neurosurgical surgeries in Iran, Islamic Republic Of with the best quality and lowest possible price
Symptoms of brain aneurysm and its rupture
Most brain aneurysms cause no symptoms and may only be discovered during tests for another, usually unrelated, condition.
…if an aneurysm presses on a vital area of the brain it may cause severe headaches, blurred vision, changes in speech, and neck pain.
However if an aneurysm presses on a vital area of the brain it may cause severe headaches, blurred vision, changes in speech, and neck pain. Once the aneurysm ruptures the patient may suffer a stroke. The severity of the stroke and extent of paralysis and speech disruption may depend on the size of the aneurysm that has ruptured.
Diagnosis is usually made by a Computed Tomography (CT) scan. It shows that extent of bleeding in the brain. Computed Tomography Angiogram (CTA) scan uses a combination of CT scanning, special computer techniques, and contrast material(dye) injected into the blood to produce images of blood vessels. It shows the blood vessel that has ruptured. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) is another more specific method of diagnosis.
Treatment brain aneurysm
If the aneurysm is small (less than 10 mm) the chance of rupture is low. Surgery for a brain aneurysm is often risky so in these cases doctors may wish to keep the patient under observation. However, if it is large or pressing on a vital area of the brain surgery may be recommended.
Surgical techniques may be of two main types. Coil embolization is a procedure where a small tube is inserted into the affected artery and positioned near the aneurysm. Tiny metal coils are then moved through the tube into the aneurysm, relieving pressure on the aneurysm and making it less likely to rupture.
This procedure is less invasive and is believed to be safer than surgical clipping, although it may not be as effective at reducing the risk of a later rupture. The other method is surgical clipping.
This involves placing a small metal clip around the base of the aneurysm to isolate it from normal blood circulation. This decreases the pressure on the aneurysm and prevents it from rupturing. Sometimes in cases of large aneurysms, they may need to be cut out and the ends of the blood vessel stitched together. This is a rare operation.