Robotic Cardiac Surgery
Introduction
Cardiac surgery may now be performed using robots. This came after the United States regulatory authority – the Food and Drugs Administration FDA – approved of robotics in cardiac surgery in around 2004. Bypass operation has been performed increasingly with the help of the device. A heart bypass operation involves opening up clogged arteries of the heart that raise risk of heart attack. During the procedure, the surgeon is able to reroute blood supply around the blocked vessels to help prevent a heart attack.
Surgical Procedure
The device – the Da Vinci Endoscopic Instrument Control System, manufactured by Intuitive Surgical Inc., of Mountain View, Calif. – has been used for gall bladder and other surgeries. Now it is used in open heart bypass surgeries. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The device is controlled by a computer and video console by the surgeon who regulates the arms of the robot within the patient’s operative site. The device has three arms that are controlled by the surgeon with handgrips and foot pedals on a console.
Robotic cardiac surgery devices have the advantage of precision, smaller incisions, less pain, decreased blood loss, and quicker healing time.
Iran is among the top 10 countries in treating cardiovascular diseases, while it ranks first in the Middle East
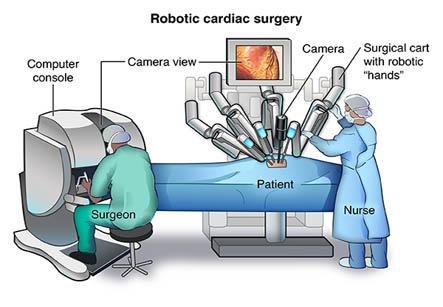
In traditional surgeries, in most cases the patient is rendered unconscious by general anesthesia. The surgery may last up to 5 or 6 hours. For an open heart procedure the chest is cut open along with the breast bone and the patient is put on a heart lung machine. This machine – during the operation works as the patient’s own heart and lungs while the surgeons work. The incision may be 10 to 12 inches long. The heart muscles are deprived of blood and oxygen during the procedure and are preserved by cooling. A robot assisted surgery may require a smaller incision leading to fewer complications after the operation.
Robot assisted surgeries are also used for repair and replacement of heart valves, correction of deranged heart rhythms or arrhythmias and atrial fibrillations. In babies and young adults who have a congenital defect in the walls separating the chambers of the heart, robotic surgery is approved for use.
Other considerations
Robotic cardiac surgery devices have the advantage of precision, smaller incisions, less pain, decreased blood loss, and quicker healing time. Additionally they provide a deeper view and more room for manipulation during the surgery. Those who have had robotic surgery recover faster, are discharged earlier, need less blood transfusions and pain medicines. Robot assisted operations have other advantages like removal of risk of naturally occurring hand tremors and continuous usage by rotating surgery teams
On the other hand cost of a robotic heart surgery is much higher than a traditional open heart surgery and not all set ups or surgeons are conversant with the procedure.
Complications with robotic cardiac surgery are similar to open heart traditional surgery but are rarer. Common complications include pain, bleeding, infections and dislodgement of blood clots. The latter may need to be prevented by taking regular blood thinners. These blood clots may get lodged in the lungs or brain leading to life threatening consequences. Complications associated with general anesthesia are also rare but present.