Minimally Invasive Surgery
Introduction
Minimal Invasive surgery is also called as Minimal Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass (MIDCAB). It is a minimal invasive technique which is an alternative to the conventional Coronary artery bypass graft surgery or CABG. MIDCAB surgery does not require stopping of the heart (cardioplegia), therefore a heart-lung machine is not required. It is a type of beating heart surgery. MIDCAB surgery has various advantages like fewer complications, less pain and faster recovery after the surgery.
Purpose of surgery:
The coronary arteries, two in number, and their branches are small blood vessels supplying the heart with oxygen and nutrients in the blood. When there is partial or complete blockage of one or more branches of these arteries due to lipid or cholesterol plaques formed in the arterial walls (atherosclerosis), the heart does not get enough blood to support the metabolism. This is called as ischemic heart disease, or coronary artery disease (CAD). And the symptom complex of this disease is called as angina in which the main symptom is chest pain.
This surgery restores the blood flow and thus, the supply of oxygen and other nutrients to the heart.
This surgery is used as one of the methods to treat coronary artery disease. When only one or two coronary arteries are to be bypassed, MIDCAB surgery is preferred. But, for bypassing three or more arteries the conventional CABG is indicated. Prior to the decision of surgery, other modalities like medical treatment as well as cardiac rehabilitation or coronary angioplasty are tried.
Iran is among the top 10 countries in treating cardiovascular diseases, while it ranks first in the Middle East
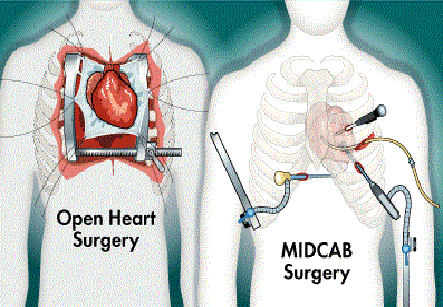
The conventional surgery requires a 10 to 12” incision for separating the breastbone or sternum and also includes a necessary heart-lung machine. But in MIDCAB, the incision is only of 3 to 5” length which is placed between the ribs. This can also be done by several small cuts.
Minimal invasive surgery on beating heart:
The challenge for the surgeon in the minimally invasive bypass surgery is that of suturing or “sewing” the arterial connection while the heart is beating. In this case, a stabilization system is required to the surgeon to stabilize only the operative area of the heart so that the surgeon can carefully stitch the bypass without any hassle. This avoids use of the heart-lung machine and its problems.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Bypass Surgery:
This surgery restores the blood flow and thus, the supply of oxygen and other nutrients to the heart. Minimally invasive bypass surgery serves the same purpose of conventional bypass surgery. However, it has many advantages for the patient as compared to CABG surgery mainly because of small incision and beating heart technique. These are:
1. Short hospital stay: patients can be discharged from the hospital in about 2 to 3 days as compared to the longer stay of about 5 to 10 days in case of conventional CABG surgery.
2. Less pain: patient has a better ability of coughing and deep breathing as the pain is less.
3. Faster recovery: there are fewer chances of complications like stroke or kidney failure in this procedure because of small incision and avoidance of the heart-lung machine. So the patient can return to the normal activities in 2 weeks rather than a long 6 to 8 weeks with conventional surgery.
4. Fewer traumas and bleeding: The use of Heart-lung machine requires removal of blood from the circulation and diverting it to the machine. For this, the patient must be put on anticoagulants or need to be given other blood products. The heart-lung machine can damage the blood cells. All these factors are avoided if the heart-lung machine is not used.
5. Low infection rate: there is less exposure and handling of the tissues due to small access. This reduces the infection of the surgical area and lungs.
6. More patients can be candidates: the minimal invasive technique allows performing bypass on high risk patients like patients with other major diseases, with coexisting heart diseases and elderly patients who cannot withstand the stress of a major surgery.
7. Cost effectiveness: the cost of minimal invasive surgery is 25% less than conventional CABG surgery.