Uterine Fibroid Embolization UFE
Introduction
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) is a procedure performed by a radiologist to block the blood flow to fibroids in the uterus. It is also called as uterine artery embolization. This procedure is an alternative for surgery for women who are not planning a pregnancy in the future.
Preparation:
The doctor’s instructions should be exactly followed about when to stop eating and drinking, or it may result in cancellation of procedure. If the doctor has instructed to take your medicines on the day of the procedure, do so using only a sip of water. A sedative may be given to the patient about an hour before the procedure for relaxation. The patient is awake during the procedure. A consent form is signed by the patient regarding permission for the procedure.
UFE has several advantages over hysterectomy, myomectomy, and treatment with GnRH-a. We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide gynaecological treatment in Iran
Procedure:
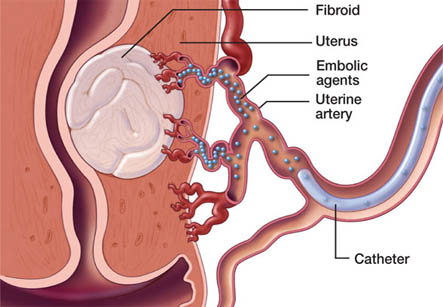
First, a thin, flexible tube called as catheter is placed into a blood vessel in the upper thigh (femoral artery). A substance called as contrast material (dye) is then injected into the catheter. A warm sensation is felt as it travels up to the uterus. The radiologist uses fluoroscopy (live X-ray) on a video screen to see the arteries and then guides the catheter to the arteries that supply blood to the fibroid. A solution containing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles is injected into those uterine arteries through the catheter. These particles build up in the targeted arteries and block blood flow to the fibroid. This causes death of abnormal cells.
After the treatment:
Uterine fibroid embolization usually takes about 1 and 3 hours, depending on how long it takes to guide the catheter and position it in the arteries in the uterus. When the procedure is over, the catheter is removed and pressure is applied to the puncture site for 10 to 15 minutes, to prevent bleeding. A bandage is then applied to cover the wound. At least 6 hours of bed rest is necessary after the procedure.
Patient is sent home after the bed rest period if the pain is under control. Sometimes, overnight stay in the hospital is recommended. Moderate to severe pelvic pain is common for 6 to 12 hours after this procedure. Narcotic pain medicines are used to control this pain, if required.
Some vaginal bleeding is expected for a couple of weeks. This is from a fibroid which is breaking down and bleeding.
In some cases, bleeding or pain persists for several months. Some women also pass a fibroid from the vagina, usually 6 weeks to 3 months after UFE. This can even occur after a year. This passage of fibroid should be immediately informed to the surgeon.
Patient can resume the usual activities in 7 to 10 days.
Recommended follow-up care includes a routine checkup 1 to 3 weeks afterward and an ultrasound or MRI 3 to 6 months later.
Indications:
Uterine fibroid embolization is used to shrink or destroy the uterine fibroids. It is used in women with fibroid, who do not wish to undergo hysterectomy, do not plan to be pregnant in the future, and have not reached menopause. Although this procedure can be done for fibroid of any size; UFE is not recommended for all types of fibroids.
In some cases of infection or uterine damage during UFE, the need of hysterectomy may arise.
Results:
UFE is an effective treatment, but fibroids may recur. This procedure reduces the size of fibroids by about 50% in most of the cases.
Approximately 80 out of 100 women treated with UFE for uterine fibroids report improvement in their symptoms. However, UFE does not always cure fibroids.
Risks
The rate of complications after UFE is low but includes:
1. Infection. This is the most serious, potentially life-threatening complication of UFE. In rare cases, hysterectomy may be required to treat an infected uterus.
2. Premature menopause.
3. Loss of menstrual periods (amenorrhea).
4. Scar tissue formation in uterus
5. Persistent pain for months.
Advantages:
UFE has several advantages over hysterectomy, myomectomy, and treatment with GnRH-a (the hormone-suppressor medicine used to shrink fibroids). These include:
1. No need of general anesthesia
2. No abdominal incision
3. No blood loss, so there is no need for blood transfusions.
4. All fibroids can be treated at the same time.
5. It does not cause bone-thinning (osteopenia) or the other serious side effects associated with GnRH-a treatment.
Disadvantages:
1. UFE is as expensive as hysterectomy.
2. An unpredictable effect on fertility, so it is not recommended for women who want to become pregnant.
3. The possibility of delayed infection, which can become life-threatening if not treated.
4. Not being a sure cure.