Colposcopy
Introduction
Colposcopy is the technique to examine the vulva, vagina, and cervix with the help of a special magnifying device known as colposcope. If some problem is suspected, small sample of tissue (biopsy) can be taken from the cervix or from the endocervical canal.
During colposcopy, the scope magnifies as well as illuminates the view of tissues and can diagnose the problems which are usually missed by the naked eye. A video monitor can be connected to the colposcope to guide the doctor and to store the examination.
Acetic acid and Lugol’s iodine solution can be applied on the vagina and cervix with a cotton swab to see problem areas more clearly.
We have all the information you need about public and private clinics and hospitals that provide gynaecological treatment in Iran
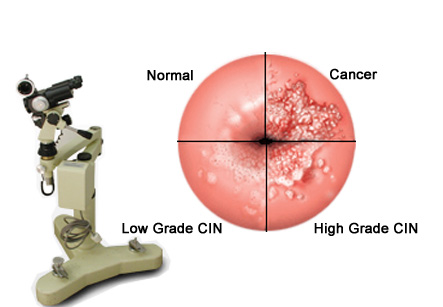
Indications:
Colposcopy is done to:
1. To examine the cervix when a Pap test is abnormal. If an abnormal area is found during colposcopy, a biopsy or small piece can be taken from the cervix or endocervical canal.
2. To diagnose genital warts in the vagina and cervix.
3. Follow up of abnormal areas seen on a previous colposcopy to see the efficacy of treatment.
4. To examine the cervix in case if HPV test shows a high-risk type of virus is present.
Preparation before colposcopy:
Before a colposcopy, the following should be informed to the doctor:
• Allergy to any medications
• Having other diseases like heart disease, diabetes or high blood pressure.
• Any medications being taken
• Any blood clotting problems or if blood-thinning agents are being taken like warfarin
• The patient is or may be pregnant.
• History of treatment for vaginal, pelvic or cervical infection.
The colposcopy is best done during the early part of your menstrual cycle or after 8 to 12 days of start of the previous menstrual period.
A consent form is signed by the patient regarding the procedure and risks involved. Sexual intercourse or putting douches, tampons or medications in vagina should be avoided for at least 24 hours before a colposcopy. Bladder should be empty.
A pain reliever, such as ibuprofen can be advised 30 to 60 minutes before having a colposcopy, especially if a biopsy is required. This can help to decrease the cramping pain caused by the colposcopy.
The colposcopy is best done during the early part of your menstrual cycle or after 8 to 12 days of start of the previous menstrual period.
Technique
1. Colposcopy is usually done by a gynecologist as an outpatient procedure.
2. Clothes should be taken off below the waist. A drape is given to cover around the waist. The position for the procedure is lying on the back on an examination table with feet raised and supported by foot rests.
3. An instrument with smooth, curved blades known as speculum is inserted in the vagina. This speculum is used to gently spread the vaginal walls apart for viewing the interior of the vagina and cervix.
4. Then, the colposcope is moved near the vagina to look inside the vagina through the microscope. Acetic acid or Lugol’s iodine solution may be used to make the abnormal areas found in the cervix more visible.
5. A small biopsy is taken if abnormal areas are found in the cervix. The samples are examined under a microscope for cancerous or precancerous changes in the cells. A special liquid or silver nitrate swab is used on the biopsy area in case of bleeding.
6. If a sample of tissue is needed from inside the opening of the cervix, a small sharp instrument is used to scrape the tissue out of cervix. This is called as endocervical curettage. It is not done during pregnancy.
7. About 15 minutes are usually required for colposcopy and cervical biopsy.
Associated risks:
In rare cases, a cervical biopsy can cause an infection or bleeding. Doctor should be contacted in case of heavy bleeding, fever or foul smelling discharge from vagina. Some vaginal soreness, bleeding or discharge is normal after biopsy for a couple of days. Sex, douching or use of tampons should be avoided for at least a week.
Significance of colposcopy:
1. An abnormal pap test in a high risk woman for cervical cancer is an indication for colposcopy.
2. If both colposcopy and cervical biopsy are normal, the probability to have precancerous changes in the cells is very low.
3. If there is discrepancy in results of Pap test, colposcopy, and cervical biopsy, a large biopsy called as cone biopsy is needed.
4. Women with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have a higher chance of developing cervical cancer. For such women, a colposcopy is highly recommended.