Appendectomy
Introduction
Appendicetomy is a surgery to remove the appendix from the abdomen. It can be performed by open method with a small incision taken over the abdomen or by laparoscopy with a small camera inserted in the abdomen.
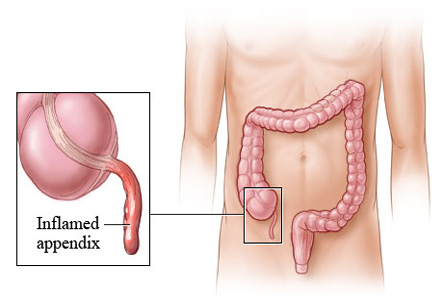
Appendix is a small worm shaped vestigial organ in human body attached to 1st part of large intestine. This organ has no function in humans. It is located in right lower side of abdomen. Inflammation of appendix is called as appendicitis. It is the most common surgical emergency. Appendectomy is a treatment of choice for acute appendicitis as well as for appendix mass and tumor of the appendix.
Appendicitis can occur at any age, but it is more common in young adults. Rarely, it can also occur in children under two years of age.
The appendix is a small, tube-shaped pouch attached to your large intestine. It's located in the lower right side of your abdomen
Symptoms of appendicitis:
1. Pain in abdomen is the hallmark symptom of appendicitis. It starts commonly in the middle of abdomen and radiates to lower right side. It can also occur in other areas if location of the appendix is different.
2. Nausea
3. Vomiting
4. Fever
5. Constipation
6. If it is not treated in time, the appendix ruptures in the abdomen. The infectious material inside the appendix spills into normally sterile peritoneum leading to severe peritonitis. Abscesses can form in the peritoneum and this may cause intestinal obstruction. Symptoms of shock, intense pain in abdomen and even death can occur in this case.
Assessment of appendicitis:
The patient can be discharged from hospital as early as 1 to 2 days after surgery if there are no other complications like perforation or abscess.
The diagnosis of appendicitis is mainly clinical and can be very tricky at times, especially in females. There are many conditions mimicking appendicitis. Laparoscopy can be used conveniently in case if the surgeon is suspecting appendicitis. It can be used for both investigation and treatment of this condition.
Surgeon cannot predict as to when the inflamed appendix ruptures. Therefore, it is prudent to remove it in case of strong suspicion based on symptoms and signs. A misdiagnosis can be possible but rare nowadays. A CT scan or barium meal tests can be done but are not very specific.
Procedure of appendicectomy:
1. The patient is given general anesthesia or regional anesthesia with sedation. Then, the surgeon cleans the skin over the site of the appendix with an antiseptic solution. A special incision known as Mc-Burney’s incision is taken over the area of appendix. The skin, underlying layers of fat and the muscle are retracted or cut to expose the appendix.
2. The blood supply of the appendix is tied off with sutures and the inflamed organ is cut from the base carefully. With purse string sutures, the base of appendix is buried in the wall of the intestine.
3. A drain may be put inside the abdomen to remove any pus or fluid collected afterwards.
4. The abdomen is closed in layers by sutures and dressing is given.
5. If the surgery is done by laparoscopy, a few smaller skin incisions are required and dissection of appendix is done inside the body. Then, the appendix is removed with special graspers.
6. The operation is complicated and lengthy in case of rupture or abscess formation. Drainage tubes are mandatory to remove the pus and fluid in a continuous manner from the surgical wound. Peritoneal washes are given to clear the infectious material from abdomen. Intravenous antibiotics are required for treatment of peritonitis.
Recovery after surgery:
The patient can be discharged from hospital as early as 1 to 2 days after surgery if there are no other complications like perforation or abscess. The pain can be managed by regular pain relievers. There is no delay in discharge if the patient does not have fever and is able to eat and drink normally. If the appendix had perforated, longer hospital stay is advised as it needs intravenous antibiotics and special precautions. Normal activities can be resumed within 1 to 3 weeks after surgery.
Risks involved in appendicectomy:
As for all surgical procedures, these include:
1. Bleeding
2. Infection
3. Damage to surrounding structures in the abdomen
4. Anesthesia related complications.
However, these risks may be considered minimal, as the peritonitis occurring due to lack of treatment of appendicitis can be fatal.