Varicose veins
Introduction
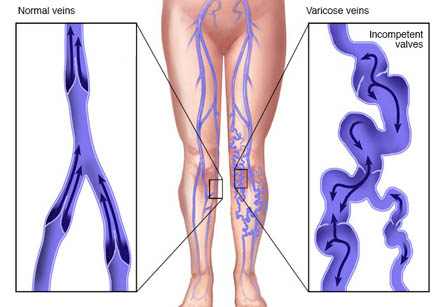
Varicose veins or varicosities are twisted, swollen, enlarged and sometimes painful veins near the surface of skin which are filled with an abnormal collection of blood.
Causes and incidence:
In any normal vein, valves in the vein maintain unidirectional (one way) flow of blood moving towards the heart. In this disease, the valves do not function properly and become incompetent. This causes pooling of blood in vein causing them to enlarge due to blood column. This process occurs mostly in the veins of lower limbs, but it can occur elsewhere too. There are various predisposing factors for varicose veins.
Varicose veins are large, raised, swollen blood vessels that twist and turn. They usually develop in the legs and can be seen through the skin
These factors include:
1. Female sex
2. Defect in valves since birth
3. Pregnancy due to uterus compressing large internal veins
4. Thrombophlebitis (inflamed veins)
5. Occupations involving standing for long time like factory workers, soldiers.
Surgical Procedure
Varicose veins may be primary or secondary. Primary varicose veins occur because of congenitally defective valves since birth or without any notable cause. Secondary varicose veins are those which occur due to another predisposing condition, such as when along standing worker or a pregnant woman develops varicosities.
There are various symptoms in varicose veins:
1. Tortuosity, Fullness, heaviness, swelling, and pain in legs. Symptoms get worsened on standing
2. enlarged veins look cosmetically unsightly
3. Brown or scaly discoloration of skin in ankle region.
4. Itching and excoriation
5. Sometimes skin ulcers that don’t heal easily (in later stages of disease). Ulcers can bleed on scratching.
6. Varicose veins can be sometimes a sign of thrombosis of deeper veins of leg which needs medical attention.
Diagnosis:
Duplex Doppler ultrasound is the most commonly used noninvasive test that can help your doctor study blood flow in your leg veins.
Physical examination and medical history are the essential tools in diagnosing varicose veins. Varicose veins can be diagnosed by doctor on inspection of leg vein appearance. Veins look dilated, tortuous and can be clumped together forming mass. This is done mostly in standing position. If a problem with the deep veins or complications are suspected based on the symptoms and examination, other tests may be advised. Other investigations which may be suggested by doctor are ultrasound examination of legs and color Doppler of the extremity. These tests are done to determine the flow of blood in veins and to rule out other disorders like clot or deep vein thrombosis. If varicose vein surgery or sclerotherapy is being considered, further examination can help to identify the location of the vein problem so that treatment will have the better chances of success. Duplex Doppler ultrasound is the most commonly used noninvasive test that can help your doctor study blood flow in your leg veins.
Treatment modalities:
As far as the treatment is concerned, it is usually noninvasive or conservative. It consists of
1. Avoid long time standing
2. Exercise regimens
3. Wear compressive elastic stalking or crape bandages(previously)
4. Limb elevation while resting
Surgical treatment is advised when:
1. Pain in legs
2. Long standing varicose veins with skin ulcers that don’t heal
3. Bleeding varicose ulcers
4. Due to high venous pressure, the fatty tissue beneath the skin hardens causing lipodermatosclerosis
5. Cosmetic reasons
Surgical treatment is vein stripping surgery in which vein perforators are marked and veins are removed by stripping. It is for complicated and long standing varicosities.
For patients who do not want surgeries there are some noninvasive methods available. Examples are:
1. Sclerotherapy this is to close the veins by sclerosants
3. Radiofrequency use
Prevention:
The best method is to avoid excess standing. If there is family history of varicosities, this is specifically advised.
Complications:
Varicosities go on worsening with long time but these complications are worth discussing.
1. Chronic ulcer due to pooling of blood. These ulcers are difficult to treat.
2. Bleeding from ruptured varicose vein
3. Inflammation, pain and scarring
You should call a doctor if any of these conditions arise:
1. Severe pain the legs
2. If the varicose veins become painful, tender or red
3. When complications arise